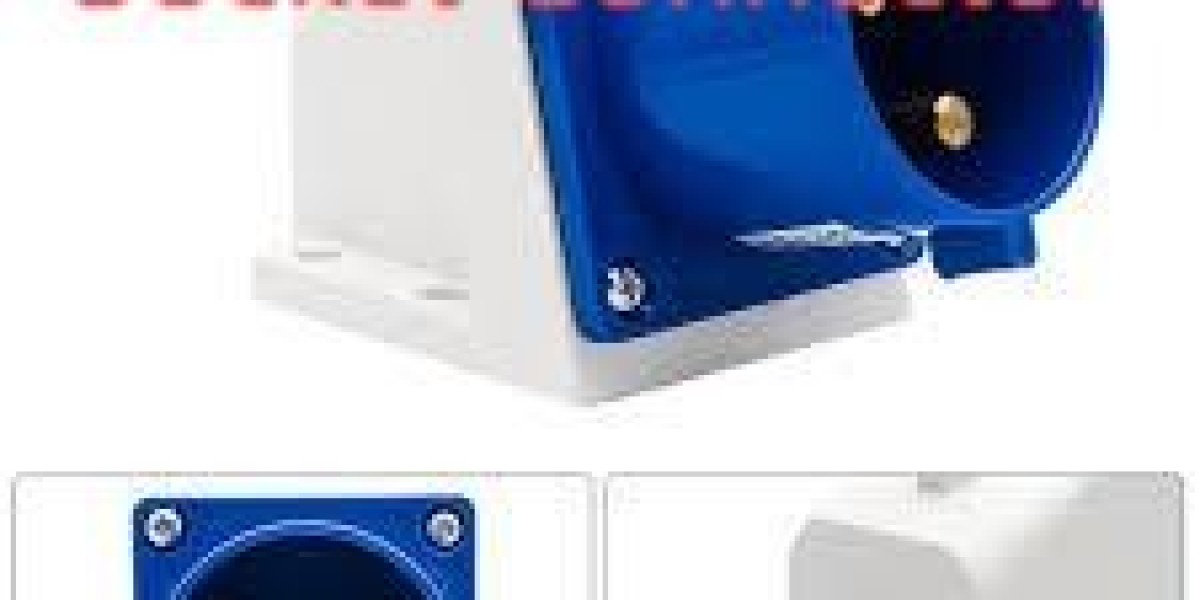
On modern job sites and factory floors where reliability matters, the Industrial Plug Socket Connector often occupies the critical mid-point between heavy equipment and stable supply, providing secure mating and straightforward service access. In many installations the Industrial Plug Socket Connector is selected for its high mating cycles, robust contacts, and ease of installation, so planners can minimize downtime and maintain consistent power delivery under demanding conditions.
Choosing the Right Contact Materials
Material science drives connector longevity. Copper alloys with specialized platings (silver, nickel, or tin depending on environment) balance conductivity and corrosion resistance. For high-current contacts, thicker cross-sections and gas-tight termination designs reduce heating and contact resistance over time. Consider the operating temperature range and potential chemical exposure when specifying contact metallurgy.
Mechanical Design and Mounting Considerations
A surface-mounted or panel-mounted connector must resist vibration, impact, and cable pull. Look for reinforced mounting flanges, captive fasteners, and strain-relief provisions that transfer mechanical loads away from internal terminations. Sealed enclosures and robust gland plates preserve ingress protection ratings, while modular faceplates simplify field swaps and reduce the need for complex rewiring during maintenance.
Thermal Performance and Current Ratings
Thermal management is essential for continuous-load applications. Specify connectors whose continuous current rating exceeds expected operating currents to avoid thermal stress. Adequate creepage and clearance, high-temperature insulators, and contact geometries that spread heat improve reliability. Thermal imaging during commissioning can reveal hotspots caused by loose connections or undersized conductors.
Schneider-Compatible Accessories and Retrofit Paths
Many facilities standardize on major industrial ecosystems; choosing Schneider-compatible accessories can simplify retrofits and spare-parts logistics. Compatibility with standard faceplates, surge modules, and locking covers minimizes custom adapters and shortens maintenance windows. Retrofit kits that preserve mounting footprints allow for upgrades without major panel redesigns, especially valuable during phased modernization projects.
Environmental Sealing and IP Ratings
Ingress protection should match the installation environment. IP67-rated connectors are suited for temporary outdoor use and washdown applications, while IP65 or IP54 may suffice indoors. Sealing systems that include double-lip gaskets, O-rings at cable entries, and corrosion-resistant hardware extend service life. For hazardous locations, verify appropriate certification (ATEX, IECEx) and select explosion-proof assemblies where required.
Wiring, Termination, and Ergonomics
Correct termination practices preserve both safety and performance. Use proper torque values on terminals, verified with torque audits, and choose strain reliefs that prevent conductor movement. Position connectors ergonomically to minimize awkward cable routing and reduce operator fatigue during frequent plug/unplug cycles. Label circuits clearly to speed troubleshooting and reduce human error.
Testing, Maintenance, and Predictive Monitoring
Develop commissioning tests that include continuity, insulation resistance, and thermal scans. Schedule periodic maintenance checks for torque, corrosion, and gasket integrity. Adding simple condition sensors — outlet temperature monitors or contact-resistance trackers — enables predictive maintenance that detects degradation before failures occur, reducing unplanned interruptions.
Lifecycle Planning and Spare Parts Strategy
Specify connectors with available spare modules and clear upgrade paths. A pragmatic spare-parts kit (inserts, gaskets, fasteners) shortens repair times. Standardizing on a small family of compatible units across a site reduces inventory complexity and makes technician training more effective, lowering mean time to repair.
Selecting and deploying the right industrial connector system requires attention to electrical, mechanical, and operational details. Prioritizing appropriate contact materials, robust mounting, thermal headroom, and environmental sealing creates a platform for dependable power delivery. For a technical overview and detailed product notes, see https://www.nante.com/news/industry-news/what-is-industrial-plug.html