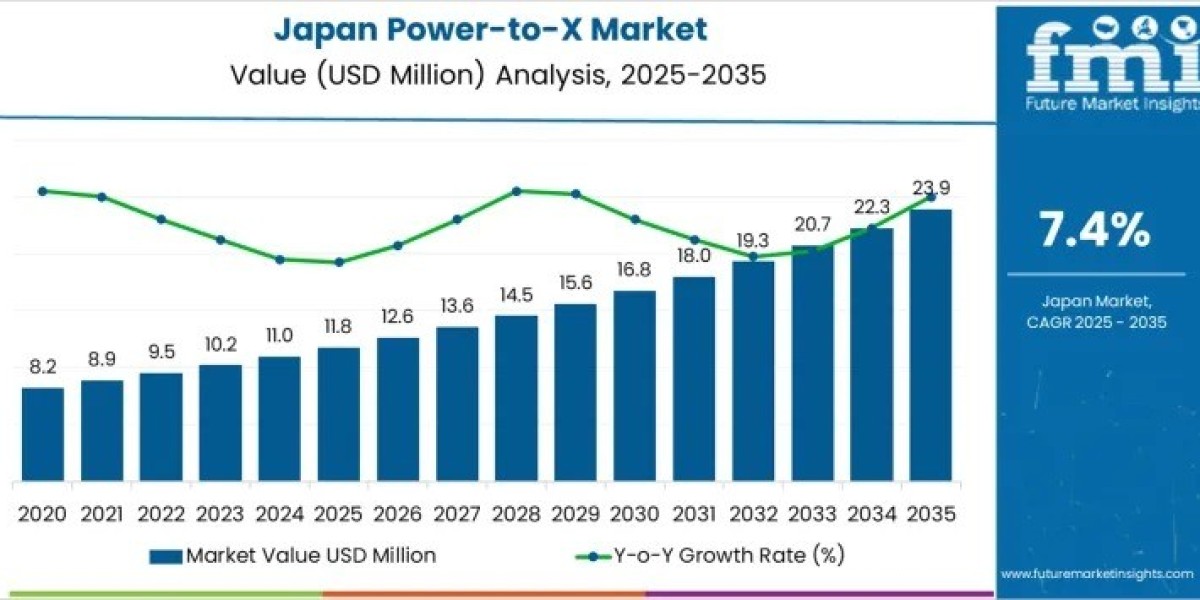
The Demand for Power-to-X in Japan is forecasted to increase from USD 11.8 million in 2025 to USD 23.9 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 7.4%. Power-to-hydrogen and Power-to-methanol pathways currently dominate project pipelines, while Power-to-methane, Power-to-H2O2, and syngas remain in pilot commercialization. Key end-use sectors include transportation, industrial energy substitution, manufacturing, and agricultural feedstock conversion. Early deployment is concentrated in Kanto and Chubu regions due to grid access and industrial clustering, with Kyushu emerging as a hub for renewable coupling projects. Leading system providers such as Siemens Energy, ITM Power, Ørsted A/S, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and NEL ASA are central to project execution and integration.
Subscribe for Year-Round Insights → Stay ahead with quarterly and annual data updates: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-29849
Key Drivers of Power-to-X Demand in Japan
- Energy Security and Decarbonization: Limited domestic fossil fuel resources and reliance on imports drive interest in converting surplus renewable electricity into transportable fuels and chemical feedstocks.
- Industrial Feedstock Stability: Steel, chemical, and refining sectors increasingly rely on synthetic hydrogen, methanol, and ammonia for continuous operations while reducing carbon exposure.
- Maritime Fuel Transition: Ports and shipping fleets adopt ammonia and synthetic methanol for compliance with emission reduction mandates, integrating Power-to-X into fueling infrastructure.
- Renewable Integration: Offshore wind and solar expansion support hydrogen production and fuel conversion, enabling energy storage and grid balancing solutions.
Regional Market Outlook
- Kyushu & Okinawa: CAGR of 9.2% through 2035, driven by solar and wind integration, green hydrogen pilots, and island energy security initiatives.
- Kanto: CAGR of 8.5%, supported by dense industrial energy consumption, port-based hydrogen import infrastructure, and private sector investment in synthetic fuels.
- Kansai: CAGR of 7.4%, anchored by industrial heat decarbonization, hydrogen mobility programs, and renewable grid integration.
- Chubu: CAGR of 6.5%, with automotive manufacturing and industrial fuel decarbonization as primary growth levers.
- Tohoku and Rest of Japan: Slower growth at 5.7% and 5.4% CAGR, reflecting gradual infrastructure development and smaller-scale renewable projects.
Product Type and End-Use Insights
- Power-to-Methanol Leads: 9.4% share of demand, benefiting from compatibility with existing fuel infrastructure and chemical feedstock networks.
- Transportation Dominates End-Use: 25.4% of market demand driven by freight, maritime, and heavy-duty mobility needs where direct electrification is limited.
- Industrial Applications: Steel, chemical, and refining sectors drive steady adoption for low-carbon feedstock and energy security.
- Residential & Distributed Pilots: Limited scale but consistent funding under regional decarbonization programs highlights growing interest in microgrid and backup energy applications.
Competitive Landscape and Project Deployment
Leading companies in Japan’s Power-to-X market focus on modular plant scalability, asset uptime, and integration with renewable energy.
- Siemens Energy: Power conversion and electrolysis integration for utility-scale projects.
- ITM Power: Electrolyzer modules for pilot and industrial facilities.
- Ørsted A/S: Upstream renewable-to-hydrogen project design expertise.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries: Hydrogen production systems and ammonia synthesis integration.
- NEL ASA: Electrolyzer systems for mobility and storage applications.
Buyers prioritize domestic engineering support, Japanese language operational capability, and proven system performance under continuous industrial load. Project selection is influenced by long-term power purchase agreements, hydrogen offtake guarantees, and alignment with national METI funding frameworks.
Outlook Through 2035
The Japanese Power-to-X market is expected to more than double in value by 2035, driven by:
- Expanding synthetic fuel demand for transportation and industrial use
- Hydrogen and methanol supply chain buildout
- Renewable integration supporting grid stability and seasonal energy balancing
- Policy-driven incentives for industrial decarbonization and maritime fuel transition
While capital intensity, grid limitations, and permitting processes constrain rapid deployment, phased investment strategies and public-private partnerships continue to ensure steady market expansion.