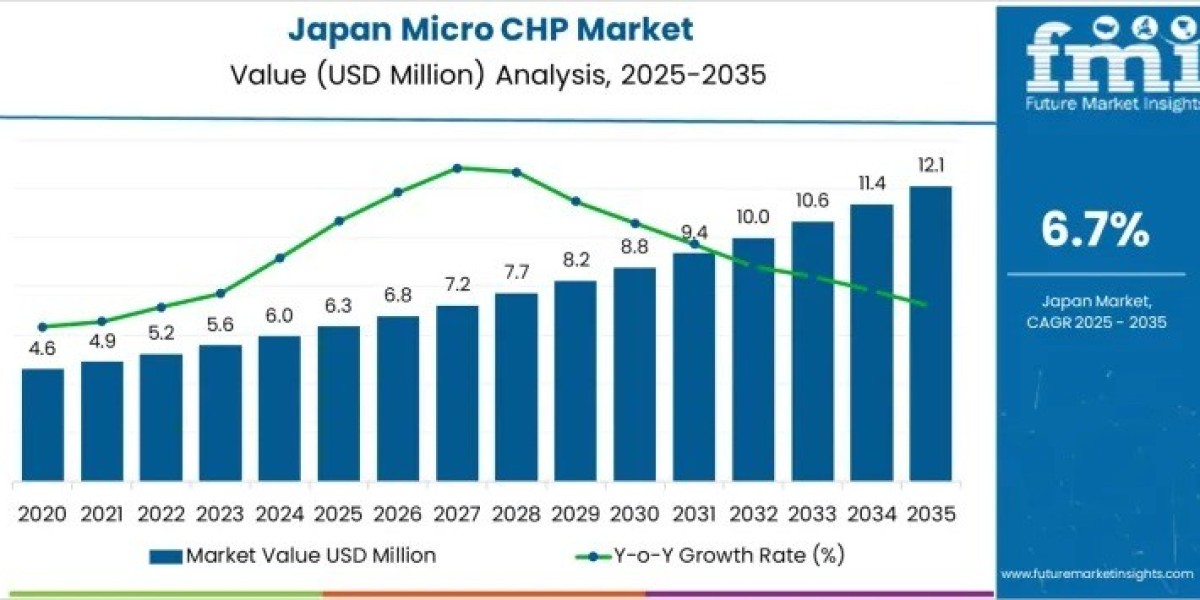
The Demand for Micro CHP in Japan is gaining sustained momentum as the country prioritizes distributed energy generation, efficiency optimization, and carbon reduction. The market is forecast to expand from USD 6.3 million in 2025 to USD 12.1 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7%.
This growth trajectory reflects Japan’s evolving energy strategy, where micro combined heat and power (CHP) systems are increasingly viewed as reliable solutions for localized electricity and heat generation. By producing both outputs from a single fuel source, micro CHP significantly improves overall energy efficiency and reduces dependence on centralized grids.
Subscribe for Year-Round Insights → Stay ahead with quarterly and annual data updates
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-29637
Residential Segment Drives Market Leadership
Residential applications dominate Japan’s micro CHP demand, accounting for approximately 60% of total market share. Rising electricity and gas prices, coupled with heightened awareness of energy efficiency, are encouraging homeowners to adopt systems that reduce long-term utility costs.
Key residential demand drivers include:
- Ability to generate electricity and heating simultaneously
- Reduced reliance on grid power during peak demand periods
- Improved energy security and resilience for households
- Compatibility with Japan’s compact urban housing structures
Micro CHP systems in the 5 kW to 10 kW capacity range are particularly popular, as they align well with the energy needs of small homes and apartments.
Stirling Engines Lead by Prime Mover
By prime mover, Stirling engines account for nearly 45% of Japan’s micro CHP demand, outperforming internal combustion engines and fuel cells. Their leadership is driven by strong alignment with Japan’s environmental and residential requirements.
Key advantages supporting Stirling engine adoption include:
- High thermal and electrical efficiency
- Low emissions and quiet operation
- Fuel flexibility, including natural gas and biomass
- Reduced maintenance requirements compared to conventional engines
These benefits make Stirling-based systems especially attractive in dense urban regions such as Kanto and Kansai, where emissions control and noise reduction are critical.
Regional Growth Patterns Reflect Policy and Urbanization
Micro CHP adoption varies by region, influenced by population density, climate conditions, and local energy initiatives.
Regional growth highlights:
- Kyushu & Okinawa lead the market with an 8.3% CAGR, driven by sustainability programs and energy efficiency awareness
- Kanto follows at 7.7% CAGR, supported by urban density, high energy demand, and decarbonization targets
- Kansai records 6.7% CAGR, benefiting from industrial activity and residential modernization
- Chubu, Tohoku, and the Rest of Japan show steady adoption as distributed energy awareness expands beyond major metros
Urban centers continue to act as early adopters, while regional incentives are gradually supporting broader nationwide penetration.
Technology Innovation Strengthens Market Viability
Ongoing technological advancements are improving the efficiency, affordability, and usability of micro CHP systems in Japan. Modern systems are increasingly integrated with smart energy management platforms, enabling real-time optimization of power and heat usage.
Notable innovation trends include:
- Improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions profiles
- Compact designs suited for space-constrained residences
- Integration with renewable and hybrid energy systems
- Enhanced reliability for continuous residential and commercial operation
These developments are expanding micro CHP’s appeal beyond early adopters to cost-conscious households and small businesses.
Key Challenges Temper, but Do Not Limit, Growth
Despite strong fundamentals, the market faces several adoption barriers. High upfront installation costs remain a concern for residential users, while system complexity can deter small commercial buyers. Additionally, competition from solar PV systems paired with battery storage presents an alternative energy pathway.
However, long-term operating savings, government incentives, and rising energy costs continue to support favorable adoption economics, ensuring steady market expansion through 2035.
Competitive Landscape and Market Participants
Japan’s micro CHP ecosystem is supported by established global players offering advanced, scalable solutions across residential and commercial applications.
Key providers include:
- ABB Ltd.
- Capstone Turbine Corporation
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Siemens AG
- General Electric Company
These companies leverage engineering expertise, distribution networks, and technology innovation to meet Japan’s growing demand for efficient, low-carbon energy solutions.
Strategic Outlook Through 2035
Japan’s long-term commitment to energy efficiency, decentralized generation, and emissions reduction positions micro CHP as a strategically important technology. As system costs decline and integration improves, adoption is expected to broaden across residential and small commercial segments, reinforcing sustained market growth.