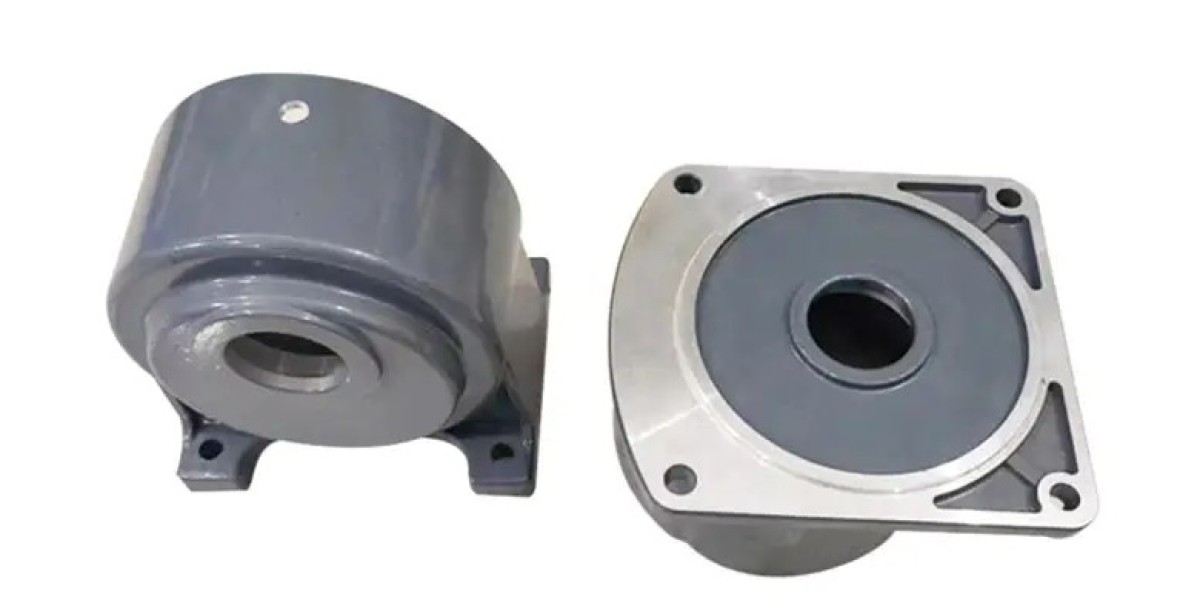
Gearbox Reducer G Series designs increasingly incorporate Automotive Aluminum Parts as manufacturers seek to balance durability with practical weight management. This approach reflects changing priorities in mechanical system design, where ease of installation, thermal behavior, and structural reliability are considered alongside traditional strength requirements.
Housing structure forms the foundation of any gearbox reducer. It supports gears, bearings, and shafts while maintaining precise alignment. Aluminum alloys used in automotive aluminum parts provide sufficient mechanical strength for housing applications when properly engineered. Their lower density compared to ferrous materials reduces overall mass without sacrificing structural stability.
Weight reduction has practical implications beyond transportation. Lighter gearboxes reduce stress on mounting frames and connected equipment. This becomes particularly relevant in modular machinery or automation systems where multiple drive units are installed along a single production line.
Dimensional accuracy is critical for gear performance. Aluminum housings support precise machining, allowing manufacturers to maintain consistent tolerances across production batches. Accurate center distances between gears reduce uneven wear and help maintain predictable transmission behavior over time.
Thermal management affects internal component lifespan. During operation, friction between gear teeth generates heat. Aluminum materials assist with heat transfer away from the gear chamber. Automotive aluminum parts used in housings help stabilize internal temperatures, supporting lubricant effectiveness and seal durability.
Environmental exposure varies widely. Some reducers operate in controlled indoor settings, while others face temperature changes or airborne particles. Aluminum surfaces can be treated with protective coatings to improve corrosion resistance. These treatments help extend service life without increasing housing thickness.
Interface design also matters. Reducers must connect accurately to motors and driven machinery. Aluminum flanges and adapter plates allow fine machining and consistent fit. Proper alignment reduces radial and axial loads on bearings, supporting smoother operation.
Structural vibration influences system performance. Gear engagement generates dynamic forces that transfer to the housing. Aluminum housings designed with reinforcement ribs can manage these forces effectively. Balanced stiffness helps control vibration transmission without creating overly rigid structures that amplify noise.
Customization capability is another benefit. Automotive aluminum parts allow manufacturers to adjust housing geometry for different Gearbox Reducer G Series models. This flexibility supports variations in shaft orientation, mounting style, and accessory placement without redesigning the entire unit.
Maintenance planning benefits from thoughtful housing design. Removable aluminum covers allow access to internal components for inspection or servicing. Reduced housing weight simplifies handling during maintenance, supporting safer working conditions for technicians.
Cost control remains relevant. Aluminum components often strike a balance between material expense and manufacturing efficiency. Established automotive aluminum supply chains contribute to consistent material quality and predictable production processes.