In today’s technology-driven world, EMC testing (Electromagnetic Compatibility testing) is essential for ensuring electronic devices operate safely and reliably without causing or suffering from electromagnetic interference. From smartphones and industrial machines to medical equipment and automotive electronics, EMC compliance is mandatory before products can enter global markets.
This comprehensive guide explains what EMC testing is, why it matters, types of tests involved, standards, procedures, costs, and how manufacturers can prepare effectively.
What Is EMC Testing?
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) refers to a device’s ability to:
Operate properly in its electromagnetic environment, and
Not generate excessive electromagnetic interference (EMI) that affects other equipment.
EMC testing evaluates both emission and immunity characteristics of electronic products to ensure they meet regulatory requirements.
In simple terms, EMC testing ensures your device doesn’t interfere with others—and isn’t easily disturbed by them.
Why EMC Testing Is Important
EMC testing is critical for several reasons:
1. Regulatory Compliance
Most countries require EMC certification before products can be sold. For example:
CE marking in Europe
FCC compliance in the United States
RCM in Australia
Without proper EMC testing, products may be denied market entry.
2. Product Reliability
Interference can cause:
Data corruption
Equipment malfunction
System shutdown
Safety hazards
EMC testing ensures consistent performance in real-world environments.
3. Customer Safety
Medical devices, automotive systems, and industrial controllers must operate safely under electromagnetic stress. EMC testing helps prevent dangerous failures.
4. Brand Reputation
A product that fails due to interference can damage brand trust and lead to recalls.
Types of EMC Testing
EMC testing is divided into two major categories:
1. Emission Testing
Emission testing measures how much electromagnetic energy a device emits.
Radiated Emissions
Tests electromagnetic waves emitted through the air.
Measured in:
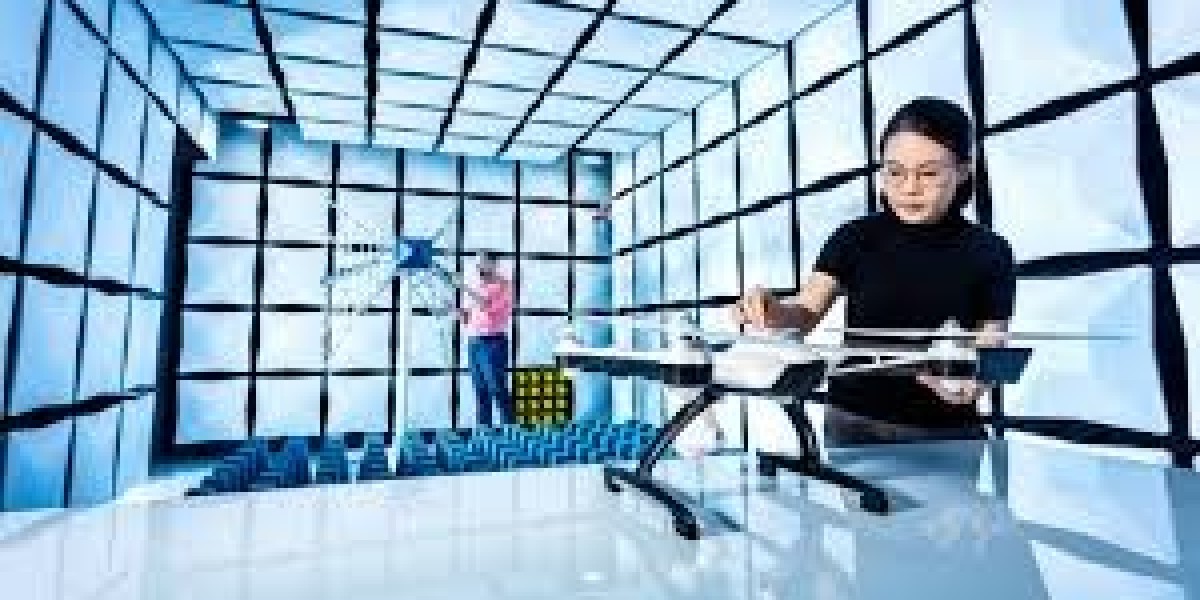
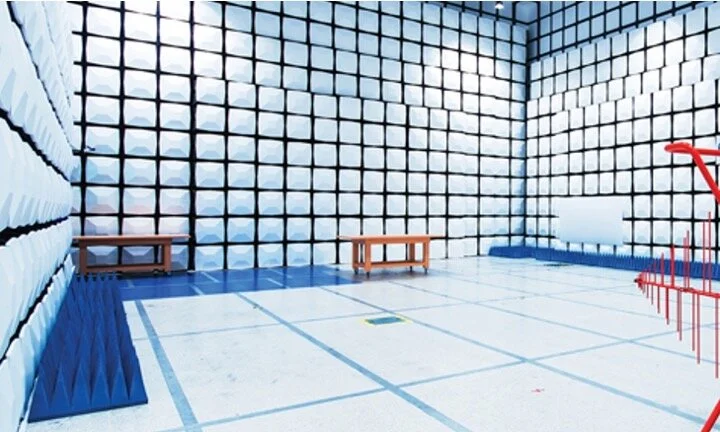
Anechoic chambers
Open area test sites
Conducted Emissions
Measures interference transmitted through:
Power lines
Signal cables
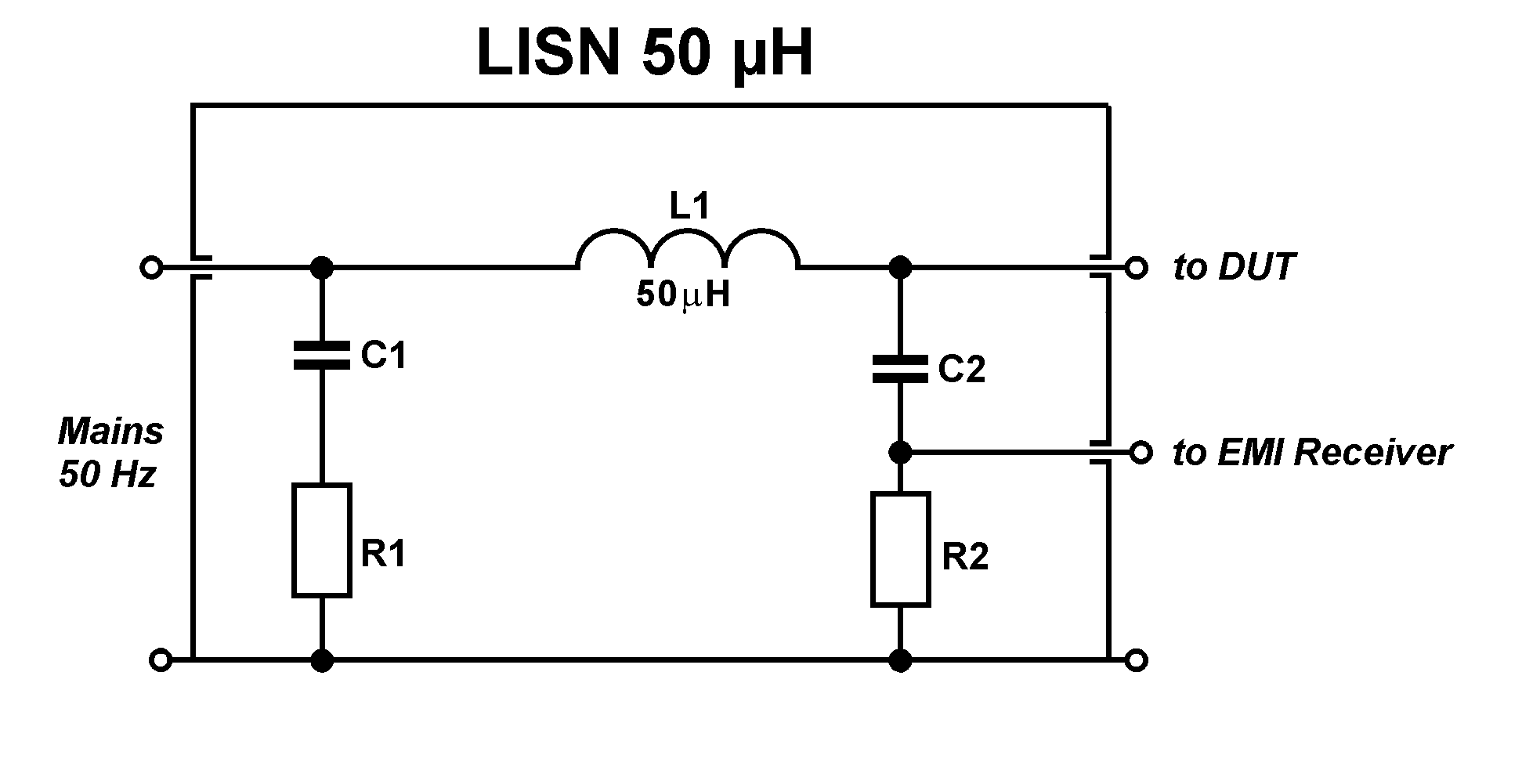
Specialized equipment like LISNs (Line Impedance Stabilization Networks) are used.
2. Immunity Testing
Immunity testing checks whether a device can withstand electromagnetic disturbances.
Common Immunity Tests:
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) – Simulates static shocks
Radiated Immunity – Exposes device to RF fields
EFT/Burst Testing – Simulates switching noise
Surge Testing – Simulates lightning or power spikes
Conducted Immunity – RF disturbances via cables
These tests simulate real-world interference conditions.
Key EMC Standards
Different industries and regions follow specific standards:
International Standards
IEC 61000 series – General EMC standards
CISPR standards – Emission requirements
United States
FCC Part 15 – For electronic devices
Europe
EMC Directive (2014/30/EU)
Automotive
ISO 11452
CISPR 25
Medical
IEC 60601-1-2
Manufacturers must select standards based on product type and target market.
EMC Testing Process
Here’s how the EMC testing process typically works:
Step 1: Pre-Compliance Testing
Internal testing to identify potential issues before official certification.
Step 2: Test Plan Development
Defines:
Applicable standards
Test levels
Test setup configuration
Step 3: Laboratory Testing
Conducted in accredited EMC laboratories using calibrated equipment.
Step 4: Reporting & Certification
After successful testing, documentation is issued for regulatory approval.
If failures occur, redesign and retesting may be required.
Common Causes of EMC Failure
Many products fail EMC testing due to:
Poor PCB layout
Inadequate grounding
Improper shielding
Long cable routing
Switching power supply noise
Lack of filtering
Early design consideration significantly reduces failure risks.
How to Prepare for EMC Testing
To improve success rates:
✔ Optimize PCB Layout
Keep signal loops small
Separate analog and digital grounds
Use proper grounding planes
✔ Add Shielding
Use metal enclosures
Shield cables
Apply ferrite cores
✔ Implement Filtering
EMI filters
Common-mode chokes
Proper decoupling capacitors
✔ Perform Pre-Testing
Testing early saves significant cost and redesign effort.
EMC Testing Cost
EMC testing costs vary depending on:
Product complexity
Test duration
Required standards
Lab location
Estimated Range:
Simple consumer device: $5,000 – $15,000
Complex industrial system: $20,000+
Pre-compliance testing reduces expensive retesting fees.
EMC vs EMI: What’s the Difference?
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) – The unwanted electromagnetic noise.
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) – The ability to function properly despite EMI.
EMI causes problems; EMC ensures immunity.
Industries That Require EMC Testing
EMC testing applies to:
Consumer electronics
Automotive systems
Aerospace equipment
Medical devices
Telecommunications
Industrial automation
Virtually every electronic product requires EMC evaluation before market release.
The Future of EMC Testing
With the rise of:
5G networks
IoT devices
Electric vehicles
Smart homes
Electromagnetic environments are becoming more complex. EMC standards are evolving to address higher frequencies and denser electronics integration.
Manufacturers must adopt robust design strategies to stay compliant.
Final Thoughts
EMC testing is not just a regulatory formality—it’s a critical quality assurance step that ensures safety, reliability, and global market access. By understanding emission and immunity requirements, following proper standards, and preparing early in the design stage, manufacturers can reduce costs and accelerate product approval.
If you’re developing electronic products, investing in proper EMC design and testing will save time, money, and reputation in the long run.